The Interstellar Cloud is Bringing Space Weather to Our Solar System

Could a thin layer of gas that is as hot as the surface of the sun affect Earth’s climate?
Our solar system, as it moves through space, is traveling through a cloud and potentially experiencing some turbulence. The Local Interstellar Cloud, or the Local Fluff as it is more colloquially referred to, is a thin layer of magnetically charged gas that is 30 lightyears across and as hot as the surface of the sun. So why hasn’t this scorching, nebulous layer of helium and hydrogen caused problems for us yet?
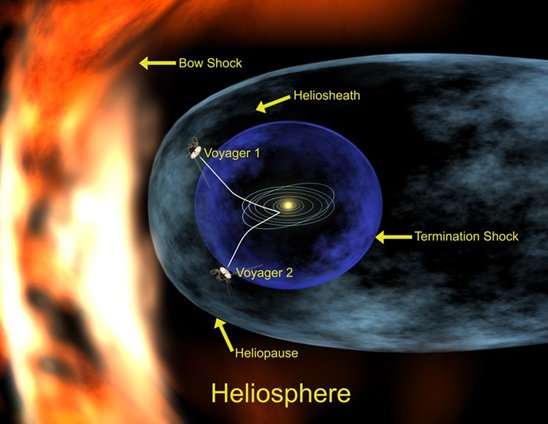
Luckily, our sun, in addition to providing us with the perfect amount of light and heat, has shielded us with a magnetic bubble that is pushed outward by the solar wind. This protective layer is known as the heliosphere and it is like a carapace for our solar system, keeping cosmic radiation and pesky interstellar fluff from fogging over our planets. But what if that protective bubble were breached, allowing for cosmic radiation to enter our solar system? We know that we experience some cosmic radiation on Earth that originates outside of our solar system, causing ozone depletion, unstable isotopes in our atmosphere, and radiation exposure at high altitudes. But we don’t know what the effects that cosmic radiation originating from the Local Fluff might have on us.
Compression of the Heliosphere
While the heliosphere and heliosheath, an area before the boundary to interstellar space, seem to be doing their jobs, there is a possibility that the Fluff is compressing our bubble. As our solar system passes through the Fluff, it becomes oblong, while simultaneously resisting the magnetic bubble of the Fluff. There is also the possibility that there are ‘cloudlets’ of significantly higher density gas within the Fluff. Could these higher density cloudlets make it through the heliosphere and into our solar system?
The average density of the Local Fluff is about 0.3 atoms per cubic centimeter. To put this into perspective, the density of the edge of Earth’s atmosphere is 12 billion atoms per cubic centimeter. At this extremely thin density, there isn’t much reason to worry about it penetrating our heliosphere, but if cloudlets of significantly higher densities came through, they could potentially burst our bubble. According to astrophysicists, these cloudlets could allow more cosmic rays to penetrate our solar system, potentially wreaking havoc on our climate. But we only have another 10,000 years before we pass through the Fluff and our cosmic sky clears.
Source: NASA
Interplanetary Climate Change
While anthropogenic causes of climate change are undeniable, there could potentially be additional outside factors at play, according to a Russian scientist named Dr. Alexey Dmitriev. This energy that is being emitted from the Fluff could be affecting all the planets in our solar system. Dmitriev believes that this energy is producing hybrid processes and excited energy states in not just the planets but also in the Sun. So, what are the consequences of this for life on Earth?
Dmitriev states that this excited state could accelerate a magnetic pole shift, it could affect ozone distribution in the atmosphere, and it could generally increase the frequency of catastrophic climate events. While this may sound apocalyptic, he says that this is a regular process and it is natural for Earth’s biosphere to undergo these changes. Essentially, Dmitriev says that these changes will create a necessity for adaptation of all life on Earth.
Whether Dmitriev’s prediction is prescient or overdramatic, we may soon have more data surrounding this phenomenon. NASA’s Voyager probes have almost breached the heliosphere to enter interstellar space, where the Fluff begins. The probes are currently in the heliosheath and able to measure the magnetic field of the Fluff. As they get closer they will hopefully be able to tell us more.
Nemesis Star Theory; Does the Sun Have an Evil Twin?

Many people remain anxious about the threat posed from a hidden nemesis planet, known as Nibiru, that has been prophesied to collide with Earth. Though many of the proposed dates for this collision have come and gone, there is another celestial body that may be more likely to lead to an apocalyptic event: The Nemesis Star.
The Nemesis Star Theory
Binary star systems occur frequently and are actually more common than single stars. At least that’s what we thought, until a recent hypothesis proposed the possibility that every star starts out as a binary pair or multi-pair system. While the theory hasn’t been confirmed, there is significant evidence that our Sun likely has a twin, an evil twin.
The majority of stars in the galaxy are red dwarfs, which are a fifth of the size of the sun and up to 50 times fainter. These types of stars are pretty commonly paired with another star in a binary system, leading astronomers to believe that Nemesis would be the Sun’s red dwarf star companion. But due to the small size and faintness of these stars, they can be hard to find, making Nemesis all the more elusive.

binary stars courtesy wired.com
This star is thought to be responsible for 12 cyclical extinction events on Earth, including the one that killed the dinosaurs. The Nemesis Star Theory’s roots can be traced to two paleontologists, David Raup and Jack Sepkoski, who noticed that there was a periodicity to major die-outs throughout Earth’s history, occurring in 26 million year intervals. This led to a number of astrophysicists and astronomers, postulating their own Nemesis Star hypotheses.
So how would the sun’s twin be responsible for mass extinctions? The Nemesis Star Theory proposed the idea that the Earth’s binary twin must be in a large 1.5 light-year orbit, retaining just enough gravitational pull between it and the Sun so as not to drift off. But the issue with the orbit of Nemesis is the possibility that it occasionally passes through a cloud of icy debris on the fringe of our solar system, known as the Oort Cloud.
Don’t Perturb the Oort
The Oort Cloud is a theoretical sphere that is believed to orbit our solar system, consisting of planetesimals, the small icy building blocks of planets, comets, and asteroids. These planetesimals are sticky and collide with each other until they become large enough to have a significant gravitational pull, eventually becoming as large as a moon or a planet. They also create asteroids and comets which can be knocked out of orbit and sent hurtling toward the center of the solar system, crashing into planets.
There is a binary star system that once passed close enough to nearly perturb the Oort, and it was likely visible from Earth. Scholz’s Star made a flyby some 70,000 years ago, at a distance of 50,000 astronomical units (AU), with one AU being the distance from Earth to the Sun. The Oort is thought to extend from anywhere between 5,000 and 100,000 AUs and is believed to contain up to two trillion celestial objects. Astronomers are 95% certain that Shulz’s star passed within half of a light-year of us, possibly perturbing the Oort, though apparently not enough to cause a mass extinction event.
Comets are believed to exist within the Oort and are the product of a thief model, a give-and-take of celestial bodies between stars when they’re formed. In this process, comets get pulled back and forth between the gravitational field of stars. It was for this reason that the Oort was theorized, due to the number of comets coming from it, there had to have been a sibling star that pulled them out to the Oort.

The Oort courtesy of space-facts.com
Astronomers also found a dwarf planet in the Kuiper Belt, a region just before the Oort that also contains icy, celestial bodies. This planet, named Sedna, orbits the Sun in a long, drawn-out elliptical path and is one of potentially hundreds. Sedna may help to explain the Nemesis star theory, in that its far-flung orbit was likely caused by our Sun’s twin, pulling it out as it drifted off into the depths of space. Imagine if instead of 9 planets in our solar system, there were a few hundred?
So where is this Nemesis star? Several years ago, the E.U. launched the wonderfully named, Gaia satellite, to map out the stars in the Milky Way and look specifically at stars that have had a close encounter with our solar system or that might come close in the future. But whether or not Nemesis will be found is unknown; it’s possible that it could make a return for the next mass extinction, or it is possible that it drifted off, perturbing the Oort of another star.




































