NASA’s Curiosity Rover Found A Strange Metallic Object on Mars

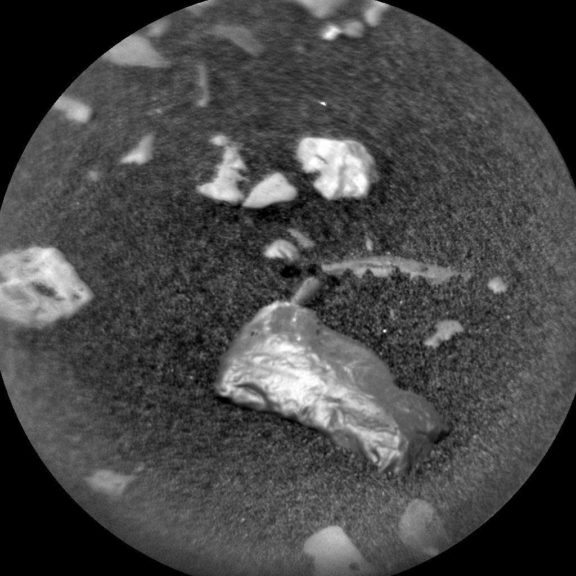
NASA’s Curiosity rover recently stumbled upon an unusually shiny object in Mars’ Gale Crater. While the discovery received some coverage, it came at a time when most attention was focused on the space agency’s successful touchdown of the InSight Lander. NASA says it believes the object may be a meteorite and that it plans to study it more closely, though Curiosity was unable to pick it up on its first attempt.
The object, which NASA named Little Colonsay after an island in Scotland, has a distinct sheen to it, even noticeable through a black and white image the agency posted on its website.
“The planning team thinks it might be a meteorite because it is so shiny,” Susanne Schwenzer, a member of the Curiosity team, wrote. “But looks can deceive, and proof will only come from the chemistry.”
Curiosity has discovered meteorites in the past, though every irregular or eye-catching find sparks excitement, especially considering the recent discovery of a 12-mile wide body of water beneath the planet’s surface — a breakthrough confirming that Mars, at some point in its past, contained vast oceans and potentially harbored life. This possibility excites those who believe we may find evidence of a lost civilization or even fossils beneath the planet’s dusty surface.

The latest discovery apparently occurred the same day the InSight Lander touched down, as NASA’s JPL website said Curiosity was greeted by the Mr. Rogers’ jingle “Please would you be my neighbor,” before it got to work studying Little Colonsay.
This is not the first time Curiosity has come across anomalous looking objects, as it once found a piece of plastic, which was later alleged to have originated as debris from its landing.
Other strange looking objects the rover uncovered have convinced people that NASA found animals or artificial remnants it then covered up or ignored. However, the space agency insists these to be the product of pareidolia – a trick our minds play on us to make objects appear recognizable – though still, some remain skeptical.
Back in August, a very distinctly shaped object was discovered by Curiosity igniting speculation of an alien artifact or that it was a piece of the rover which was starting to fall apart. NASA tried to quell the excitement saying it tested the object and found it was a rock.
In other instances, online sleuths have claimed that the rover imaged animals including a squirrel and a duck on the Martian surface. These claims however, should probably be taken with a grain of salt, but if you’re interested you can find them here and here.
Even if most of Curiosity’s discoveries are just rocks, there are in fact, some truly unexplained anomalies discovered while observing the red planet – check them out in this episode of Deep Space :
How to Prepare for Upcoming Solar and Lunar Eclipses

Eclipse season will be here soon, here’s what you can expect and how to prepare for this cosmic dance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
Both solar and lunar eclipses hold strong energy in astrology. They can shake us up and stimulate change within ourselves to reach our highest power. We will soon see a partial solar eclipse and a lunar eclipse. What can we expect from these cosmic events?
“Eclipses take place when we have lunar events, which are full moons or new moons that fall close to the nodal axis,” Astrologer Mercedes Arnus Arraut said. “So what is the nodal axis? The nodal axis is the axis of intersection between the orbit of the moon around the Earth and the orbit of Earth around the Sun. That intersection has a north and south, and those points are called nodes. So, the north node represents our destiny; or future, where we’re headed as humanity, what is our destination, what is our direction, where do we need to focus on. In the south, the south node represents our past; what we need to purge, what we need to cleanse, what we need to integrate, what we need to let go…”.
The first eclipse will be on April 30, but Arraut says we will feel it a lot sooner.
“We usually start feeling it around a month before the first eclipse takes place. So, this first eclipse that takes place, the 30th of April, brings many changes into our lives, since all eclipses are like catalysts that align us with our highest purpose. Eclipses literally will cleanse, detox, and be used as tools to show us what path we need to follow,” Arraut said.
Soon after the solar eclipse,we will see a lunar eclipse in May. How does this relate to the solar eclipse we just had?