Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu Wants to Clone Scythian Army

The Russian military is reportedly looking to clone ancient warriors. Is it possible, and if so, why would they do it?
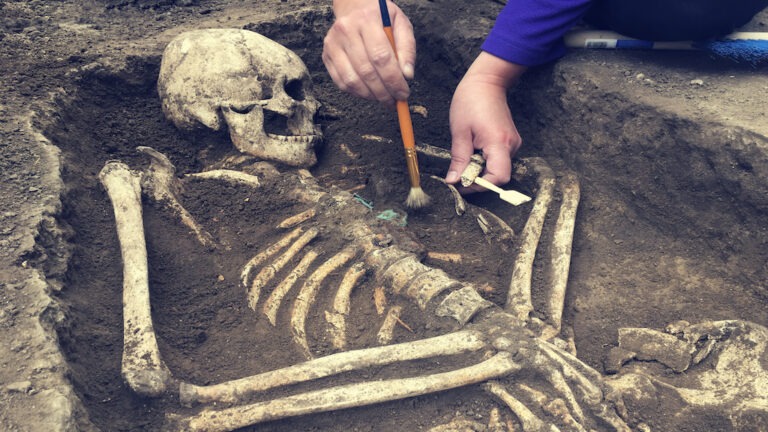
In the Siberian Republic of Tuva lie the remains of Scythian warriors and their horses buried for nearly 3,000 years. Now, Russia’s Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu apparently wants to put them back into action.
According to Ancient Origins, Shoigu has announced his desire to clone the 3,000-year-old soldiers telling the Russian Geographical Society, “Of course, we would like very much to find the organic matter and I believe you understand what would follow that. It would be possible to make something of it, if not Dolly the Sheep. In general, it will be very interesting.”
Dolly the Sheep refers to the first mammal ever cloned back in 1996. Now, a Russian-Swiss archeological team is reportedly searching for viable DNA from the graves to clone the ancient warriors. But many scientists are skeptical that this is even possible. No human has ever been cloned—that we know of…
Watch more:
Mysterious Geoglyphs in India Are Largest Ever Discovered
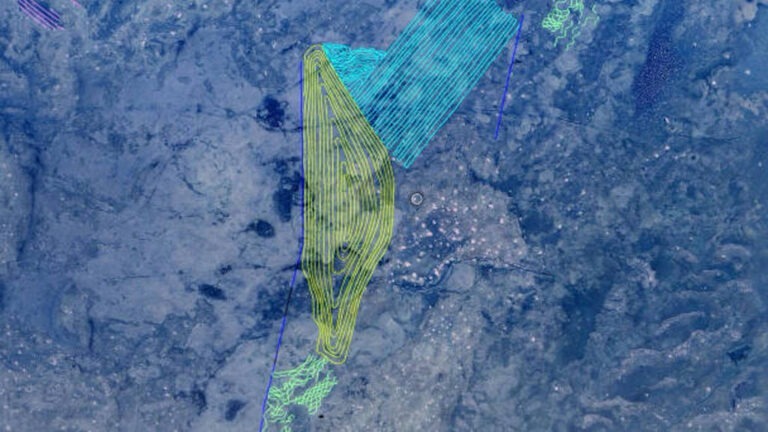
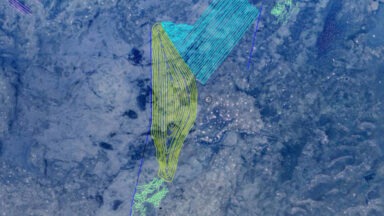
Researchers discovered the world’s largest geoglyphs in the Great Indian Desert. Will their findings reveal who made these giant, enigmatic designs, and why?
Geoglyphs are sprawling designs made by digging into the Earth or piling up stones to form what mostly appear as geometric lines, and more rarely, as humans and animals.
Usually only fully visible from above, they can be found all over the world with some dating back to prehistoric times, and others quite recent. The most famous to date are the Nazca lines in Peru. While there are various theories around their builders and function, none have been proven and continue to be widely debated.
Carlo Oetheimer is an independent researcher of geomorphology, the study of Earth’s landforms. While conducting a Google Earth survey of India, he and his son Yohann Oetheimer, made a fascinating discovery.
“I was traveling all over the desert, and suddenly I found lines in the desert similar to the Nazca lines. I was amazed, and I said, ‘Oh, what’s that?’ I found one place, then two places, then eight places almost. That was the way I found the Thar Desert Boha geoglyphs,” C. Oetheimer said.
“So, under Google Earth’s images, we could see a concentric spiral — concentric lines. We didn’t really know at that point what they were, but we had to go on the site, on the field, to understand them better,” Y. Oetheimer said.
When the researchers visited the desert site in India’s Rajasthan region, what they found astounded them.
“We brought a drone with us to be able to take aerial photos of the geoglyphs. With the drone images we could finally see the true form of the line, which is a spiral,” Y. Oetheimer said.