What are the Paracas Skulls? Explore the Ancient Mystery.

The Paracas skulls are a massive collection of ancient, elongated skulls discovered on Peru’s south coast. Julio Tello, a Peruvian archaeologist, made the discovery in 1928, when he recovered more than 300 elongated skulls from the Paracas desert peninsula.
While elongated skulls are not a new phenomenon, the Paracas skulls are particularly curious for three reasons: They are the largest elongated skulls found anywhere on Earth; they contain mysterious, unknown DNA; and they are structurally different from other elongated human skulls that have been found.
Theories Behind the Paracas Skulls
There are several theories of how the Paracas skulls came to be:
Artificial cranial deformation
Artificial cranial deformation, known more commonly as head binding or head flattening, is an ancient technique in which an infant’s head is manually deformed to create an elongated shape. This is accomplished by placing the child’s head between two pieces of wood over a prolonged time period.
Why would someone do such a thing? It’s believed ancient peoples associated the elongated head shape with spiritual or social status, making it a desirable trait.
There is abundant evidence that certain cultures utilized this practice (and some still do so today). However, the Paracas skulls are distinct from those found in other cultures because of their structure and their genetic makeup.
Genetics
There is some evidence a genetic mutation gave the Paracas skulls their elongated appearance.
DNA tests show the skulls contain a foreign, never-before-seen genetic mutation. Is it possible this mutation caused the skulls to elongate? Perhaps it is the same genetic mutation that caused the hair color of the Paracas peoples to mutate as well — some of the discovered Paracas skulls have red or blond hair, which has no explanation other than genetics.
Extraterrestrials
With regard to the mysterious genetic mutation, there is another school of thought: The Paracas skulls belonged to the Nephilim, or at least some sort of unknown human-like creature.
In addition to the unknown DNA, the skulls have another curious feature that supports the theory that they are not fully human: the location of the foramen magnum, or the hole in the skull that the spinal cord passes through.
According to researcher L.A. Marzulli, the foramen magnum on the Paracas skulls is located on a spot that’s lower than where it should be. While some may assume this to be a side effect of head binding, this is misleading. Head binding and similar practices only change the shape of the skull; they do not alter other aspects of the skull’s structure.
The foramen magnum isn’t the only structural feature that stands out on the skulls. The Paracas skulls are also “25 percent larger and 60 percent heavier” than typical human skulls, and they contain only one parietal plate instead of two. Clearly, there are some distinct structural differences that make the Paracas skulls a curious anomaly.
Is it possible the Paracas skulls have a correlation to “Ata,” the nickname of a 6-inch humanoid found in the Atacama Desert in Chile? Ata also sports an elongated skull, as well as a diminutive stature and other physical abnormalities. With such evidence, along with the fact that Ata also was discovered in South America, it’s possible the Paracas skulls and the tiny skeleton have much in common.
The Paracas Skulls: Unsolved Mystery?
There are several sound theories about the origins of the Paracas skulls. While scientists have conducted extensive research on the skulls, there is always more to explore.
Conventional news outlets and think tanks are quick to dismiss anything out of the ordinary, which is why it’s important to do your own research and come to your own conclusions.
Want more like this article?
Don’t miss Ancient Civilizations on Gaia to journey through humanity’s suppressed origins and examine the secret code left behind by our ancestors.
Ireland's Newgrange Tomb; A Megalithic Hub of Mystical Curiosity
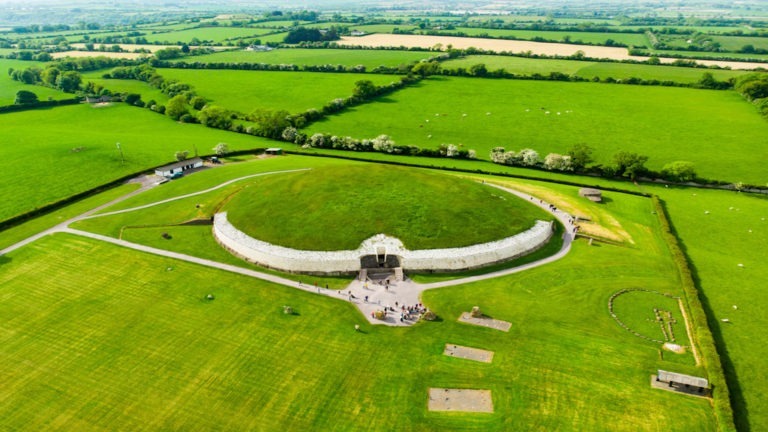

Built 5200 years ago, and during the Neolithic period (tail end of the Stone Age), the Newgrange megalithic tomb was constructed with alternating layers of dirt and rock and infused with the mystical curiosities. This earthen temple is 600 years older than Egypt’s Giza Pyramids and 1000 years older than Stonehenge. The building of Newgrange is a remarkable architectural feat. And some say it’s within one of the most popular flight paths for UFOs.
With a mesmerizing entrance stone, the Newgrange passage and tomb are adorned with beautiful circles, spirals, and radials. While the purpose of this ancient art appears to be decorative, many spiritually-minded scholars believe these etchings to be energy-creating emblems or metaphoric icons that relate to the sun, moon, and stars.
Healers and empaths say that Newgrange has an etheric quality to it, with remnants of energetic bodies no longer living in this physical reality. They believe the site to be a reservoir of healing energy for all walks of life.
Residents of the nearby Laytown say that unusual objects have been crisscrossing the night sky for as long as they can remember. More recently, unexplained crop circles have been appearing in neighboring areas. It seems the Gods are restless and trying to communicate.